About AMR and R package
R package to simplify the analysis and prediction of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) and to work with microbial and antimicrobial data and properties, by using evidence-based methods. Copyright by: https://msberends.github.io/AMR/index.html#copyright
Outine
- R packages installation
- Import CSV data
- Find frequency by variables
- Find resistance percentages
- Find resistance percentages by organism and number of isolates
- Calculate empiric susceptibility
- Calculate empiric susceptibility - Percentage
- Plotting results and compare susceptibility by antibiotics
- Yearly isolates summary - Bar chart
1. R packages installation
Open your R-Studio and install the following packages:
install.packages(c("dplyr", "ggplot2", "AMR", "cleaner"))
After successful installtion, Import the libraries:
library(dplyr) library(ggplot2) library(AMR) library(cleaner)
2. Import CSV data
# Import excel/csv data
data_sample <- read.csv("Your-file-location/amr-sample-data-r-analysis.csv")
head(data_sample) # AMK = Amikacin, AMC = Amoxicillin / Clavulanic Acid, CIP = Ciprofloxacin,
# CTX = cefotaxime, SXT = Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole, CRO = Ceftriaxone
Output:
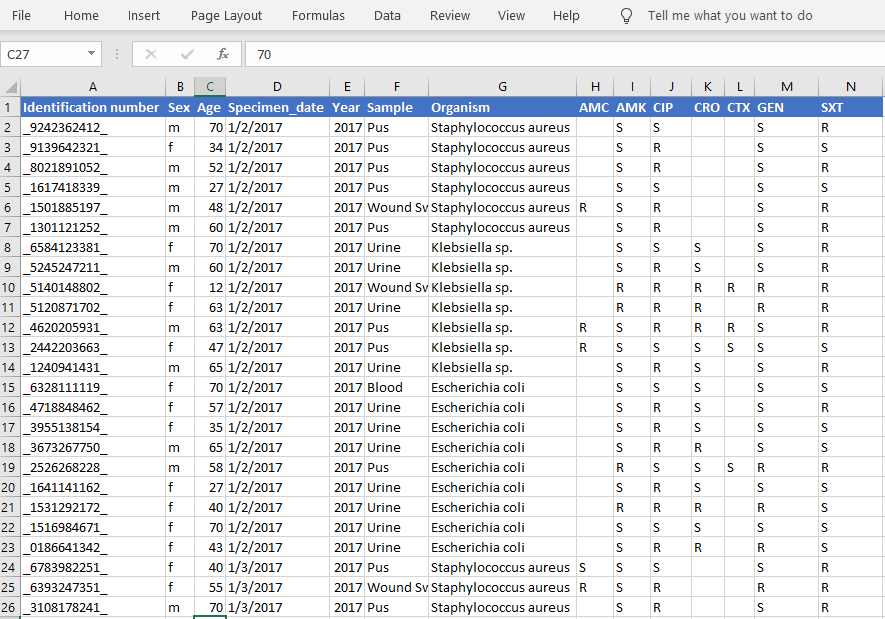
3. Find frequency by variables
data_sample %>% freq(Sex)
data_sample %>% freq(Organism)
data_sample %>% freq(Sample)
Output-Sex:
Frequency table
Class: character
Length: 23,411
Available: 23,411 (100.0%, NA: 0 = 0.0%)
Unique: 2
Shortest: 1
Longest: 1
Item Count Percent Cum. Count Cum. Percent
--- ------ -------- --------- ------------ --------------
1 f 13,568 57.96% 13,568 57.96%
2 m 9,843 42.04% 23,411 100.00%
Output-Organism:
Frequency table
Class: character
Length: 23,411
Available: 23,411 (100.0%, NA: 0 = 0.0%)
Unique: 3
Shortest: 14
Longest: 21
Item Count Percent Cum. Count Cum. Percent
--- ----------------------- -------- --------- ------------ --------------
1 Escherichia coli 11,887 50.78% 11,887 50.78%
2 Klebsiella sp. 7,709 32.93% 19,596 83.70%
3 Staphylococcus aureus 3,815 16.30% 23,411 100.00%
Output-Sample:
Frequency table
Class: character
Length: 23,411
Available: 23,411 (100.0%, NA: 0 = 0.0%)
Unique: 6
Shortest: 3
Longest: 10
Item Count Percent Cum. Count Cum. Percent
--- ------------ -------- --------- ------------ --------------
1 Urine 12,814 54.73% 12,814 54.73%
2 Pus 5,753 24.57% 18,567 79.31%
3 Wound Swab 2,549 10.89% 21,116 90.20%
4 Blood 1,214 5.19% 22,330 95.38%
5 Sputum 1,079 4.61% 23,409 99.99%
6 Stool 2 0.01% 23,411 100.00%
4. Overview of different bug/drug combinations
# Number of isolates in different bug/drug combinations
data_sample %>%
bug_drug_combinations() %>%
head(100) # show 100 rows
Results:
mo ab S I R total
1 E. coli AMC 3163 0 8484 11647
2 E. coli AMK 10541 2 1215 11758
3 E. coli CIP 3148 0 8710 11858
4 E. coli CRO 3741 0 8118 11859
5 E. coli CTX 483 0 1575 2058
6 E. coli GEN 9301 0 2487 11788
7 E. coli SXT 5408 1 6438 11847
8 Klebsiella AMC 2261 0 5360 7621
9 Klebsiella AMK 4818 1 2843 7662
10 Klebsiella CIP 2777 6 4904 7687
11 Klebsiella CRO 2626 0 5054 7680
12 Klebsiella CTX 1358 0 3799 5157
13 Klebsiella GEN 4461 0 3182 7643
14 Klebsiella SXT 2984 0 4687 7671
15 S. aureus AMC 2208 0 1388 3596
16 S. aureus AMK 3476 0 291 3767
17 S. aureus CIP 1228 0 2573 3801
18 S. aureus CRO 6 0 2 8
19 S. aureus CTX 2 0 3 5
20 S. aureus GEN 3359 0 422 3781
21 S. aureus SXT 2523 0 1272 3795
# For `aminoglycosides()` using column 'GEN' (gentamicin)
data_sample %>%
select(col_mo, aminoglycosides()) %>%
bug_drug_combinations()
Result:
mo ab S I R total
1 E. coli AMK 10541 2 1215 11758
2 E. coli GEN 9301 0 2487 11788
3 Klebsiella AMK 4818 1 2843 7662
4 Klebsiella GEN 4461 0 3182 7643
5 S. aureus AMK 3476 0 291 3767
6 S. aureus GEN 3359 0 422 3781
5. Find resistance percentages
data_sample %>% resistance(AMC) Output: 0.6662001
6. Find resistance percentages by organism and number of isolates
data_sample %>%
group_by(Organism) %>%
summarise(amoxiclav = resistance(AMC),
#amoxiclav_isolates = n_rsi(AMC),
gentamicin = resistance(GEN),
#gentamicin_isolates = n_rsi(GEN),
ciprofloxacin = resistance(CIP),
#ciprofloxacin_isolates = n_rsi(CIP)
)
Output:
Organism amoxiclav gentamicin ciprofloxacin
1 Escherichia coli 0.728 0.211 0.735
2 Klebsiella sp. 0.703 0.416 0.638
3 Staphylococcus aureus 0.386 0.112 0.677
-----------------------------------------------------------
# Total number of isolates responsible for the percentages by group (S, I or R)
data_sample %>%
group_by(col_mo) %>%
summarise(amoxiclav = resistance(AMC),
#amoxiclav_isolates = n_rsi(AMC),
gentamicin = resistance(GEN),
#gentamicin_isolates = n_rsi(GEN),
ciprofloxacin = resistance(CIP),
#ciprofloxacin_isolates = n_rsi(CIP)
total_isolates = n_rsi(SXT))
Output:
col_mo amoxiclav gentamicin ciprofloxacin total_isolates
1 B_ESCHR_COLI 0.728 0.211 0.735 11847
2 B_KLBSL 0.703 0.416 0.638 7671
3 B_STPHY_AURS 0.386 0.112 0.677 3795
-----------------------------------------------------------
# For the resistance within certain antibiotic classes, use a antibiotic class selector
such as penicillins(), which automatically will include the columns AMX and AMC of our data
data_sample %>%
summarise(across(penicillins(), resistance, as_percent = TRUE)) %>%
rename_with(set_ab_names, penicillins())
Output:
amoxicillin_clavulanic_acid
1 66.6%
-----------------------------------------------------------
7. Calculate empiric susceptibility: Get the proportion of multiple antibiotics, to calculate empiric susceptibility of combination therapies
data_sample %>%
group_by(Organism) %>%
summarise(amoxiclav = susceptibility(AMC),
gentamicin = susceptibility(GEN),
amoxiclav_genta = susceptibility(AMC, GEN))
Output:
Organism amoxiclav gentamicin amoxiclav_genta
1 Escherichia coli 0.272 0.789 0.804
2 Klebsiella sp. 0.297 0.584 0.592
3 Staphylococcus aureus 0.614 0.888 0.907
8. Calculate empiric susceptibility - Percentage
data_sample %>% group_by(Organism) %>% summarise(across(penicillins(), resistance, as_percent = TRUE)) Output: Organism AMC 1 Escherichia coli 72.8% 2 Klebsiella sp. 70.3% 3 Staphylococcus aureus 38.6%
9. Plotting results and compare susceptibility by antibiotics
data_sample %>%
group_by(Organism) %>%
summarise("1. Amoxi/clav" = susceptibility(AMC),
"2. Gentamicin" = susceptibility(GEN),
"3. Ciprofloxacin" = susceptibility(CIP),
"4. Cefotaxime" = susceptibility(CTX),
"5. Ceftriaxone" = susceptibility(CRO),
"6. Amoxi/clav + genta" = susceptibility(AMC, GEN)) %>%
tidyr::pivot_longer(-Organism, names_to = "antibiotic") %>%
ggplot(aes(x = Organism,
y = value,
fill = antibiotic)) +
geom_col(position = "dodge2")
Output:
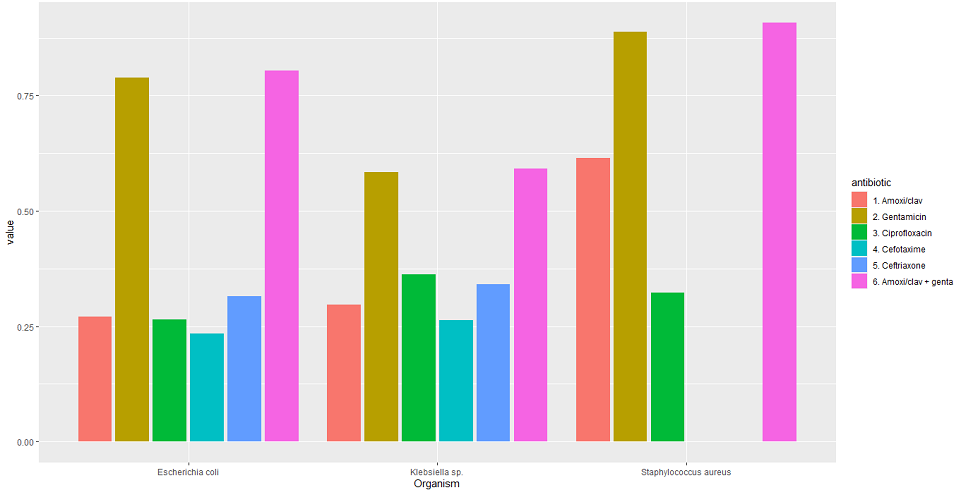
10. Stacked bars for SI and R
ggplot(data_sample) + geom_rsi(translate_ab = FALSE Output: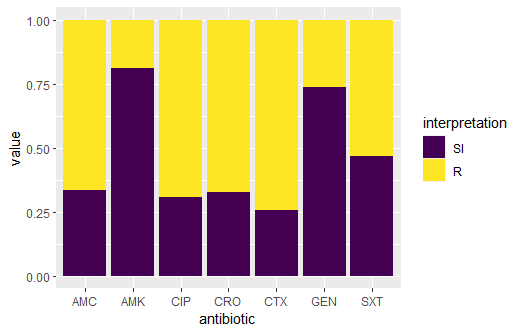
11. Resistance per genus and antibiotic
# group the data on `genus` ggplot(data_sample %>% group_by(col_mo)) + geom_rsi(x = "col_mo") + facet_rsi(facet = "antibiotic") + # set colours to the R/SI interpretations (colour-blind friendly) scale_rsi_colours() + # show percentages on y axis scale_y_percent(breaks = 0:4 * 25) + # turn 90 degrees, to make it bars instead of columns coord_flip() + # add labels labs(title = "Resistance per genus and antibiotic") # and print genus in italic to follow our convention # (is now y axis because we turned the plot) theme(axis.text.y = element_text(face = "italic")) Output: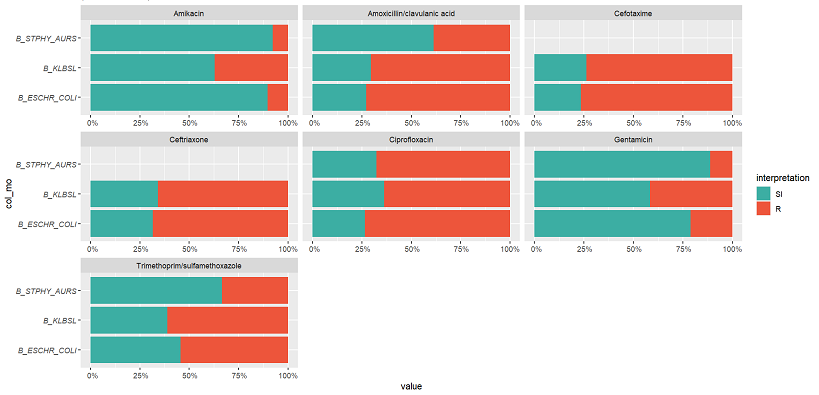
12. Yearly isolates summary - Bar chart
ggplot(data_sample) + geom_bar(aes(Year)) Output: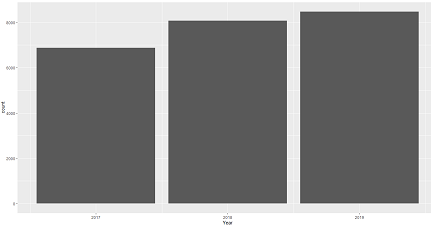
Source: https://msberends.github.io/AMR/articles/AMR.html