DHIS2 Portfolio
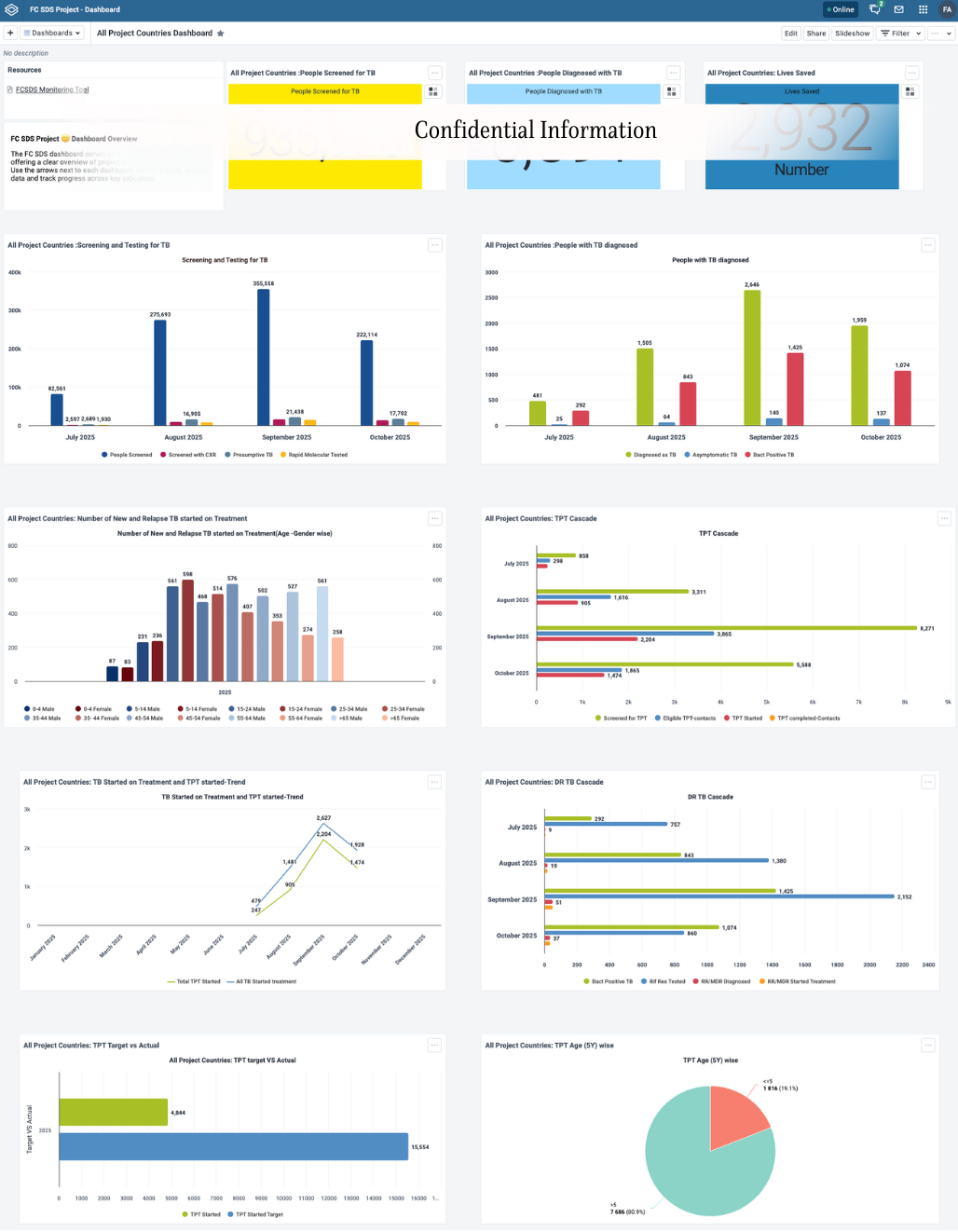
Multi-Country TB Monitoring System
Client: Stop TB Partnership, UNOPS
Location: Bangladesh, Cambodia, Mozambique, Philippines, Tajikistan
A DHIS2-based digital monitoring and reporting system has been designed and developed to strengthen tuberculosis (TB) prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and care across multiple countries. The platform supports real-time data collection, seamless integration with national systems, and advanced analytics, enabling both programmatic and financial indicators to be monitored within a unified environment. Julhas, as part of JBRSOFT’s collaboration, has provided technical assistance in installing and configuring the required datasets, ensuring the system functions optimally within country contexts. Key features include interactive dashboards, automated data exchange, and AI-assisted narrative reporting—enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and data-driven decision-making. This initiative marks an important step toward improved TB program management, greater accountability, and evidence-based planning at national and regional levels.
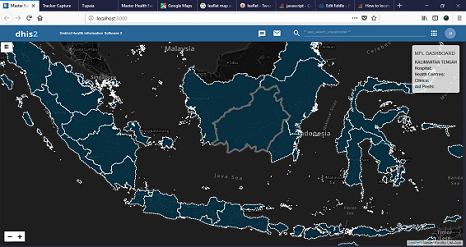
This project involves building a robust DHIS2 Master Facility List (MFL) to enhance oversight and management of health facilities in Central Jakarta. The platform supports visualization across four hierarchical facility levels, allowing administrators to plan and allocate resources more effectively.
The solution integrates service, resource, and administrative data domains into a single interface, ensuring accurate and consistent facility information. This centralized system promotes better coordination across health programs and strengthens decision-making at district and provincial levels.
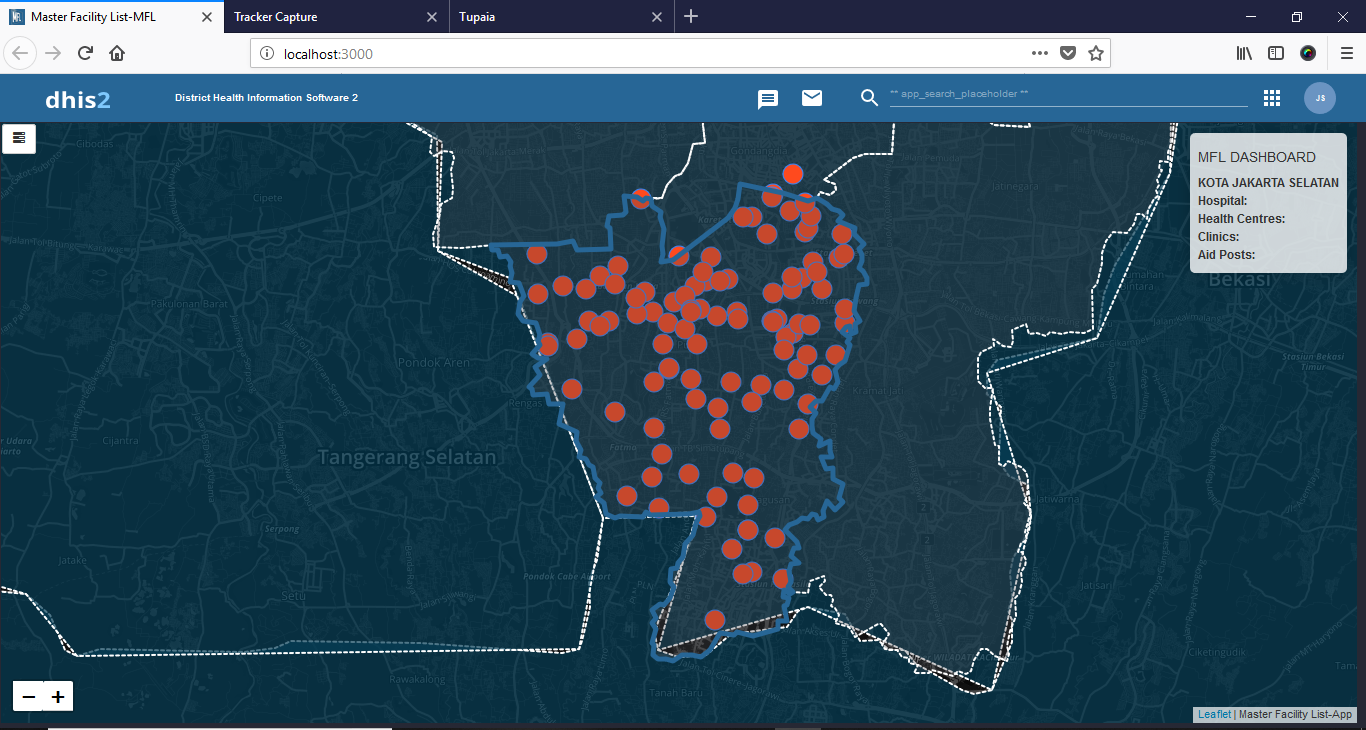
This initiative strengthens health facility management through a DHIS2-based Master Facility List, enabling detailed visualization of all four facility tiers. Users can easily navigate and analyze facilities for effective administrative and operational planning.
Integration of service, resource, and administrative information ensures that facility records remain current and accurate. The system enhances data interoperability, supports program coordination, and allows decision-makers to access comprehensive facility insights in real time.
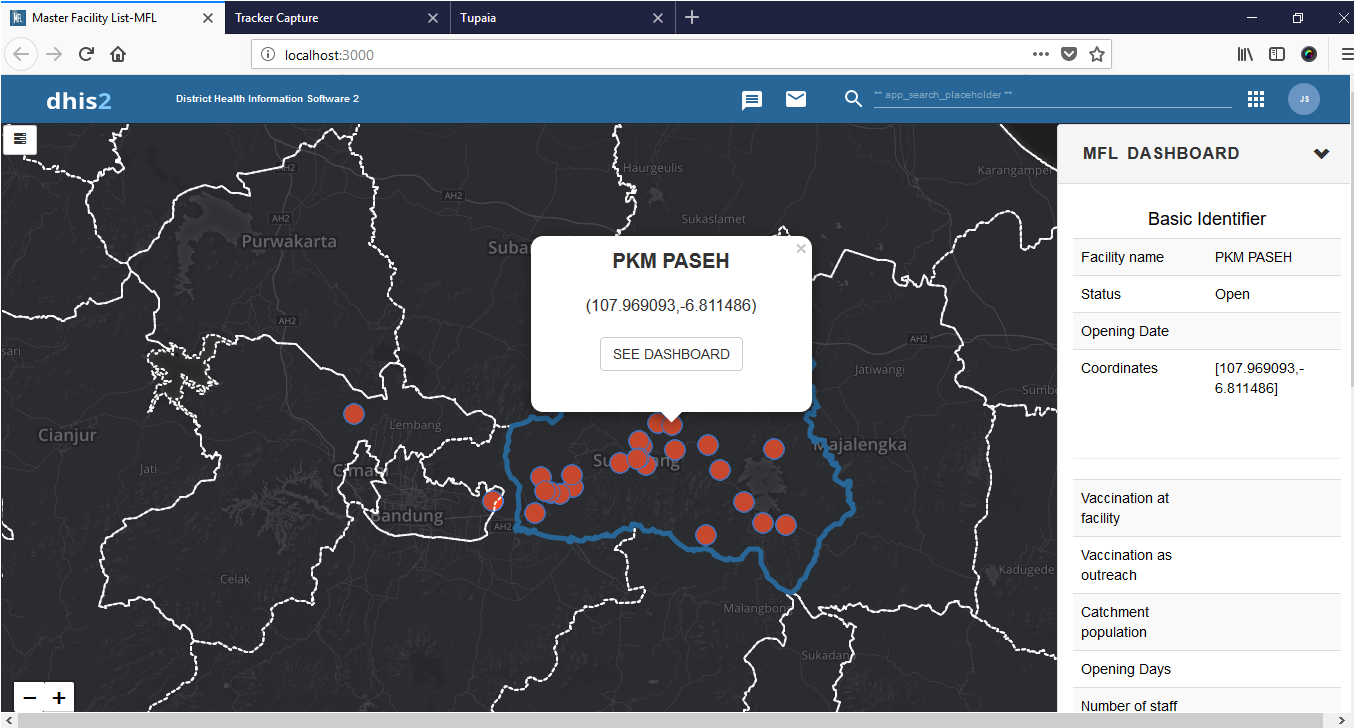
The project delivers a DHIS2 Master Facility List that provides comprehensive visualization of health facilities across four hierarchical levels. Individual facility details are easily accessible through an intuitive sidebar, enabling precise monitoring and management.
By integrating service, resource, and administrative domains, the platform ensures consistent and reliable facility information. This improves data quality, simplifies updates, and enhances collaboration across various health programs for better district-level governance.
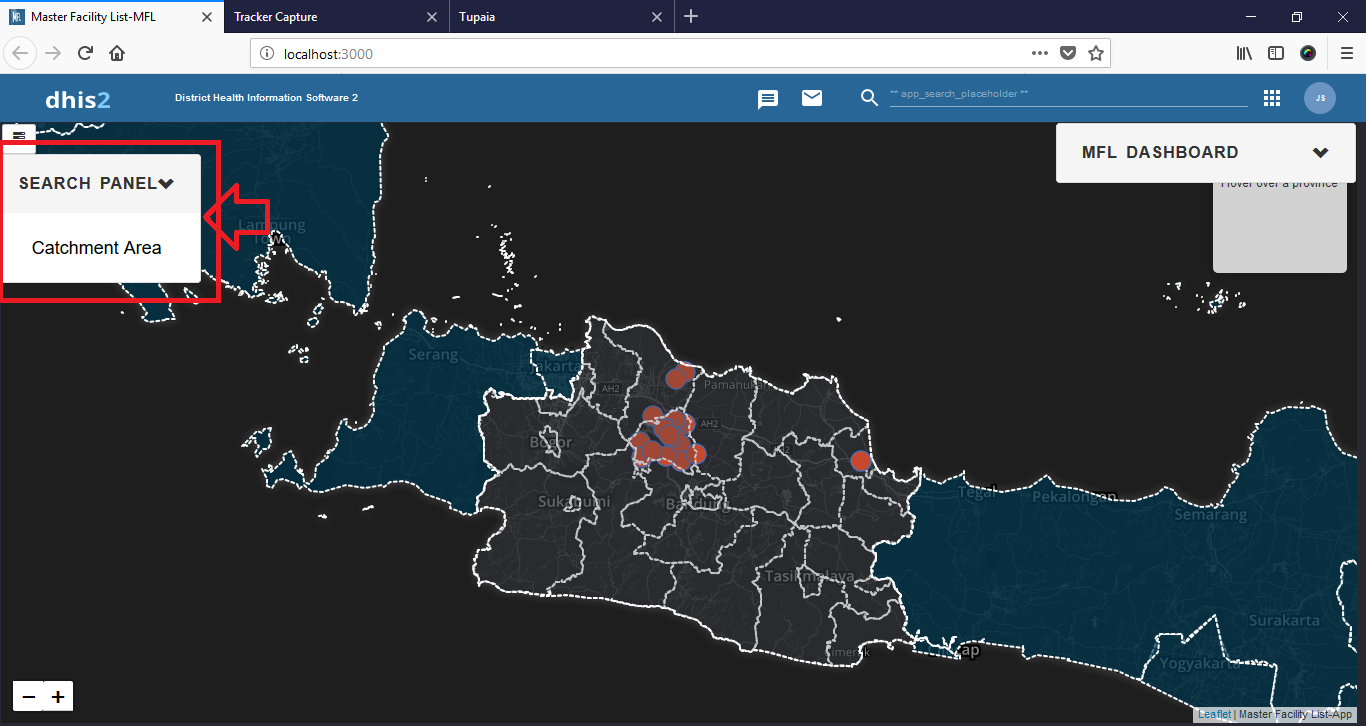
This DHIS2 MFL project enhances facility management by offering a searchable interface for quick access to any health facility across Central Jakarta. The system provides hierarchical visualization, enabling efficient tracking and decision-making.
Consolidation of service, resource, and administrative data domains ensures comprehensive and accurate facility information. The platform supports coordinated program oversight, timely updates, and improved governance across district and provincial health operations.
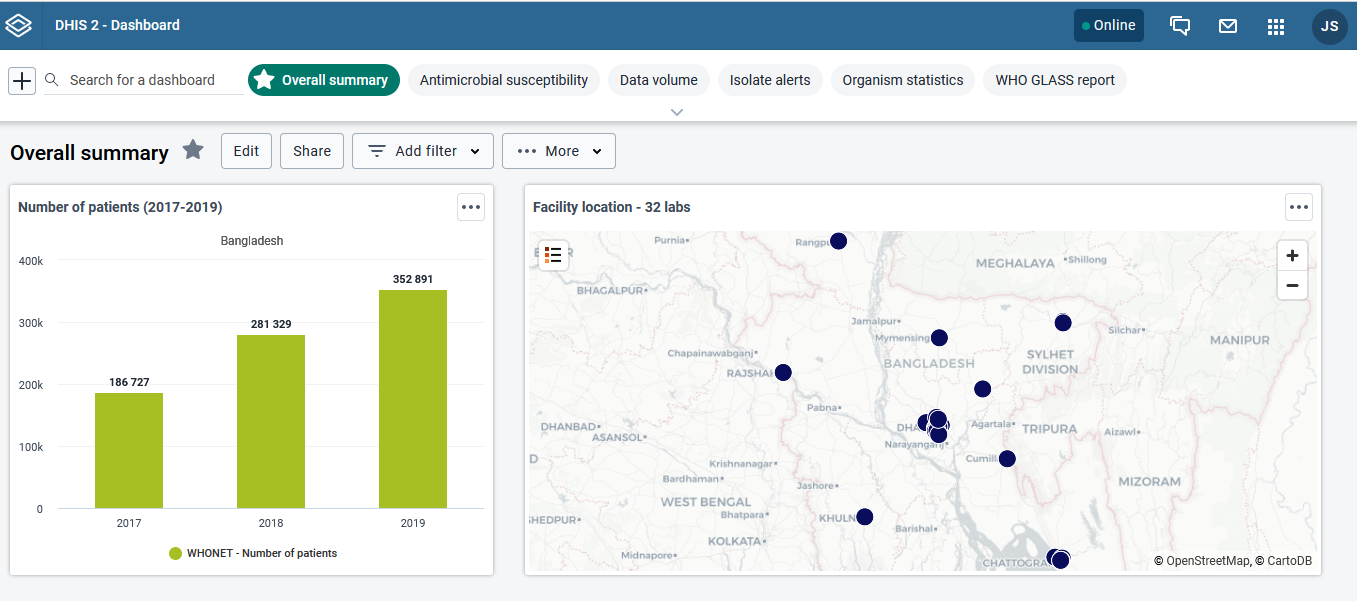
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is an emerging public health threat causing significant morbidity, mortality, and healthcare costs especially in low- and medium-income countries, but to date few groups have explored advanced AMR data management within DHIS2. In this work, we describe a collaboration between the Bangladesh Ministry of Health and Family Welfare’s Directorate General of Health Services (DGHS), the CAPTURA Project (Capturing Data on Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns and Trends in Use in Regions of Asia) led by the International Vaccine Institute (Republic of Korea) supported by the UK Department of Health Fleming Fund, and the WHONET development team at the WHO Collaborating Centre for Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance (United States).
WHONET, www.whonet.org, is a free software promoted by the World Health Organization supporting local, national, regional, and international resistance surveillance activities in over 2,500 human, animal, and food microbiology laboratories in over 130 countries. WHONET supports advanced automated features for interpretation of antimicrobial susceptibility test measurements by CLSI and EUCAST standards; multidrug-resistance profiles; 190 public health, clinical, and quality control isolate alerts; and statistical detection of hospital and community outbreaks using SaTScan. WHONET supports international guidelines for the management of “repeat” isolates, e.g. “first isolate per patient per species per data stratification and data subset”, which is not supported by DHIS2 core functionality. WHONET’s import tool BacLink permits the capture and standardization (ETL-extract, transform, and load) of microbiology data from diverse laboratory information systems, test instruments, and desktop applications.
To support WHONET and DHIS2 interoperability, we have developed pre-defined and user-defined data export options of two types: 1) aggregate statistics (and associated metadata) to DHIS2 Data Sets; and 2) isolate listings (and associated metadata) to DHIS2 Event Programs. These WHONET listing and analysis exports can be visualized within DHIS2 dashboards, pivot tables, charts, and maps. Metadata exports are consistent across all WHONET installations, permitting simple data exchange between DHIS2 instances.
In Bangladesh, we have installed WHONET in 31 laboratories and trained more than 140 microbiologists, clinicians, IT staff, and national AMR policymakers. Three years of laboratory data from 41 governmental and private hospitals in eight divisions are being submitted to the DGHS AMR-dedicated DHIS2 server through the WHONET-DHIS2 interoperability features described, leveraging both WHONET’s advanced data management and alert capabilities for AMR data with existing Bangladesh DHIS2 platforms for web-based visualization for all communicable diseases supporting the development, implementation, monitoring, and impact evaluation in near real-time of national resistance containment strategies.
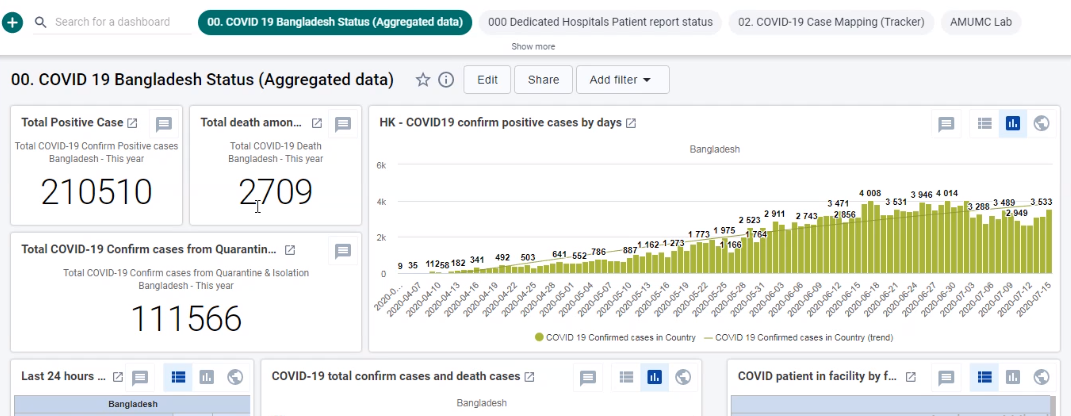
This project focused on establishing a robust DHIS2-based digital system to strengthen COVID-19 surveillance, case reporting, and real-time decision-making. The work included end-to-end installation and configuration of DHIS2, customizing tracker programs to align with national and international surveillance standards, and integrating essential workflows for case investigation, laboratory results, contact tracing, and follow-up monitoring.
The implementation ensured seamless data flow, user-friendly interfaces, and high system performance to support epidemiologists, surveillance officers, and public health managers. Comprehensive training sessions were provided for administrators and end-users to ensure effective system adoption and sustainable use. The solution enhanced data quality, timeliness, and reporting accuracy—supporting more efficient COVID-19 response operations.
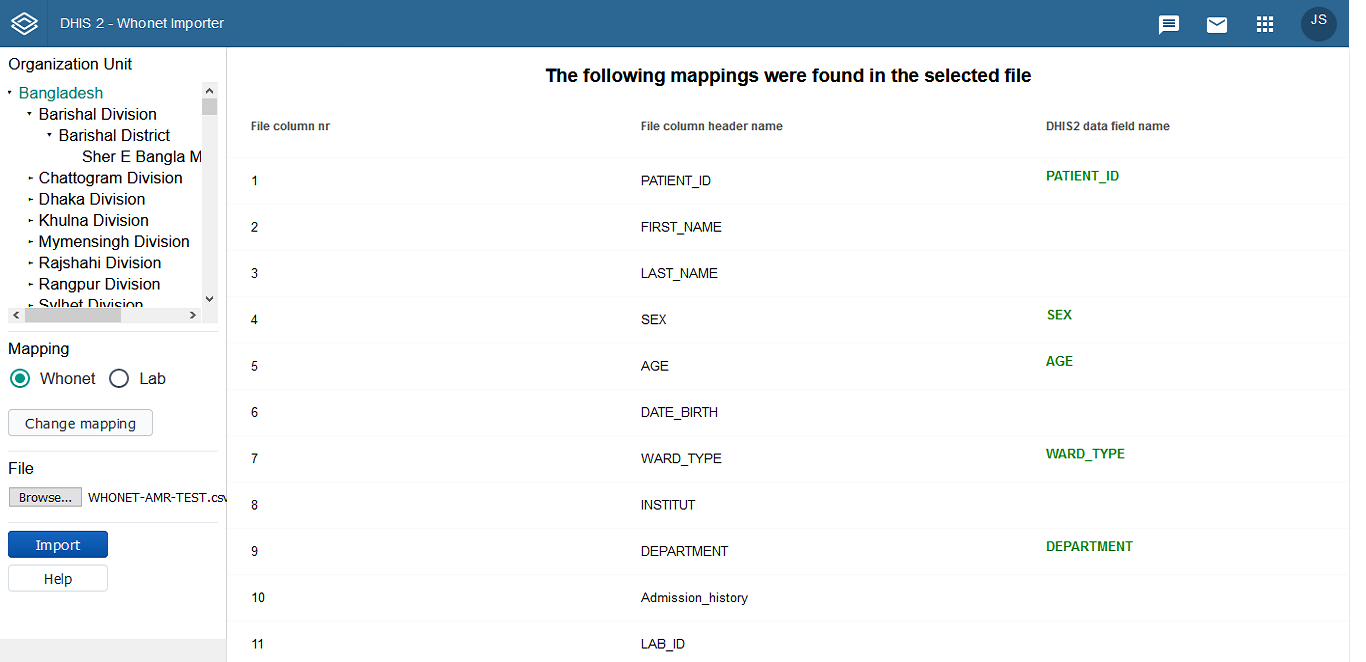
Currently in DHIS2 application, the programs are created as per organism groups. When the data needs to be imported from WHONET, it will be difficult to identify the program since it will need to first look at organism isolated and then identify the respective program which does not look feasible. An easier way out will be to create a single program for all the organisms containing all antibiotics. All the data to be imported can be imported in this single program and then the same aggregation logic can be used to aggregating data as is followed for organism group specific programs. Thus the columns heads in WHONET file will need to be mapped to the attributes and data elements in 'AMR data import' program.
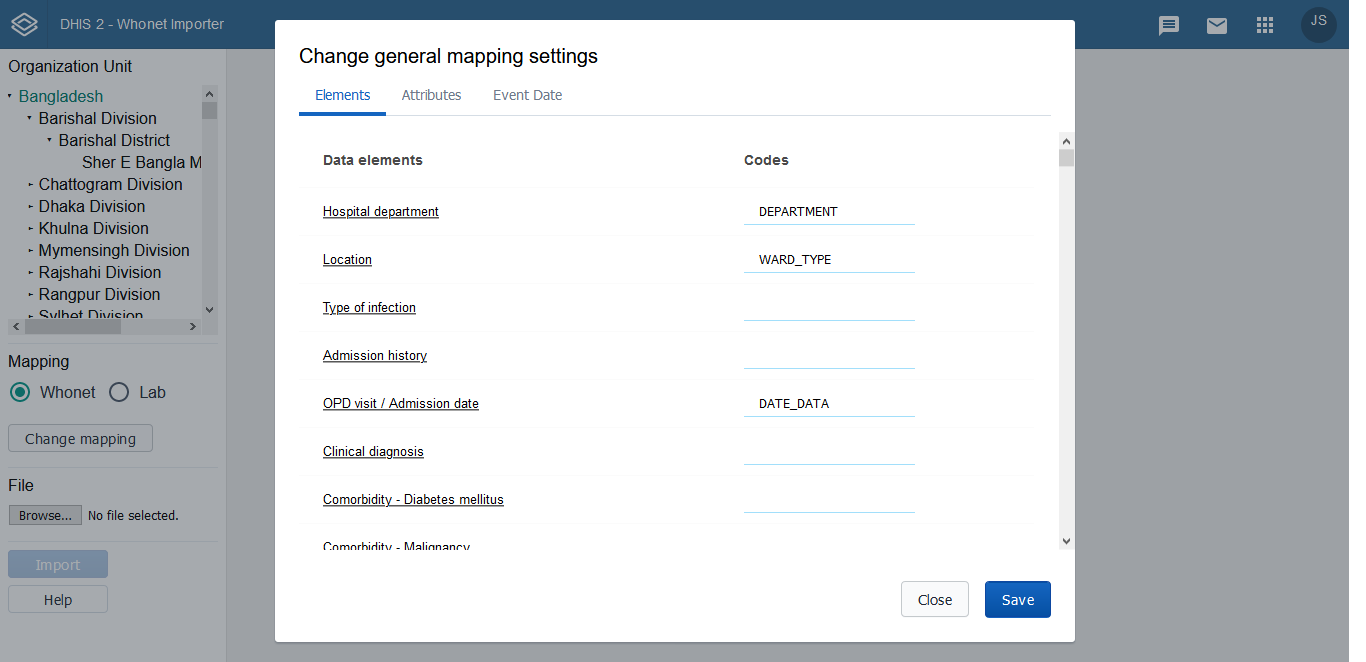
The project focuses on streamlining the import of AMR data from WHONET into DHIS2. Traditionally, DHIS2 programs are organized by organism groups, which makes identifying the correct program for import cumbersome. To simplify this process, a consolidated program was created that accommodates all organisms and antibiotics. This approach allows all WHONET data to be imported into a single program, while maintaining the existing aggregation logic for reporting and analysis. Column headers in WHONET files are systematically mapped to DHIS2 attributes and data elements in the "AMR data import" program to ensure accuracy.
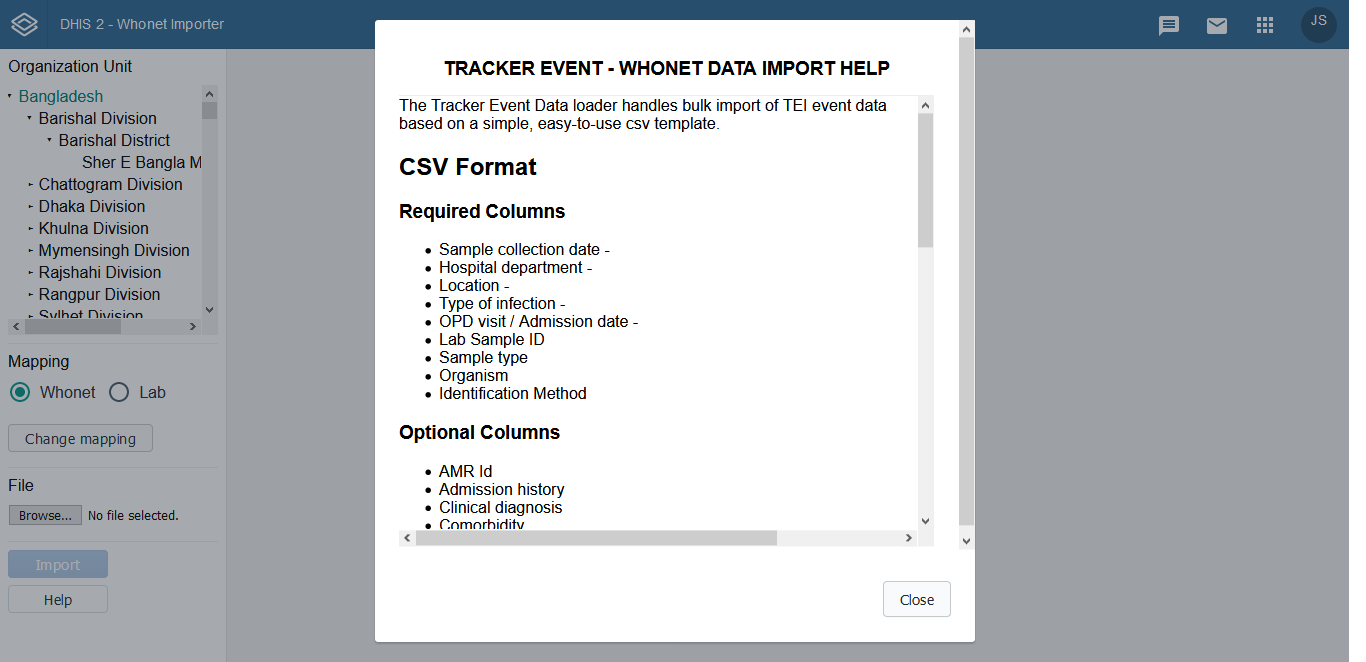
This initiative addresses the challenges of importing laboratory AMR data from WHONET into DHIS2 efficiently. Instead of mapping each organism-specific program individually, a unified program was implemented that captures all organisms and their respective antibiotics. The import workflow ensures proper mapping of WHONET columns to DHIS2 data elements, automates aggregation, and reduces manual errors. The solution provides a scalable approach for ongoing AMR data integration, supporting reliable reporting and analysis for national surveillance programs.
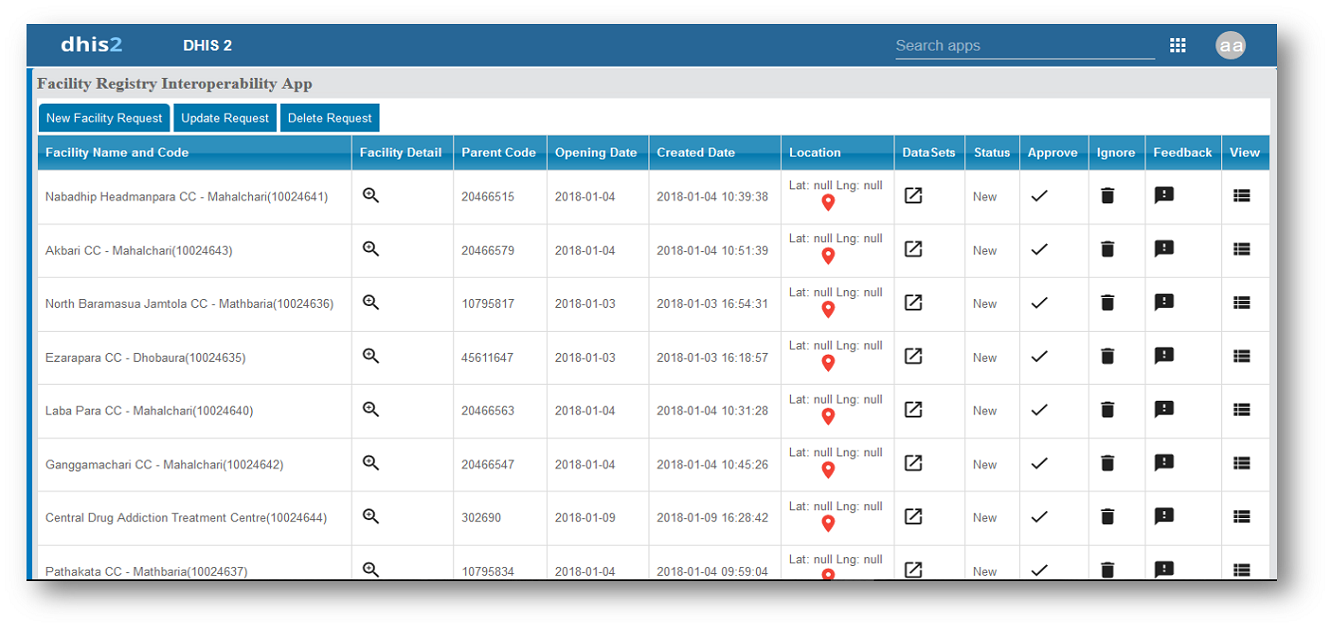
This project focused on strengthening interoperability between the Human Resource Information System (HRIS) and multiple DHIS2 instances through a dedicated dashboard and middleware services. The solution enables seamless two-way exchange of HR and facility-related data, ensuring that updates—such as new facility entries, modifications, or deletions—are accurately reflected across integrated systems.
Key features include automated handling of incomplete or blank DHIS2 facility records, a centralized notification center for system alerts, and GIS-based mapping to visualize facility locations. The interoperability layer supports both automated and manual data transfer modes, accommodates multiple DHIS2 instances simultaneously, and provides a real-time log monitoring interface to track all data transactions.
Overall, the dashboard enhances data consistency, improves system coordination, and supports streamlined HR and facility management processes across national health information platforms.
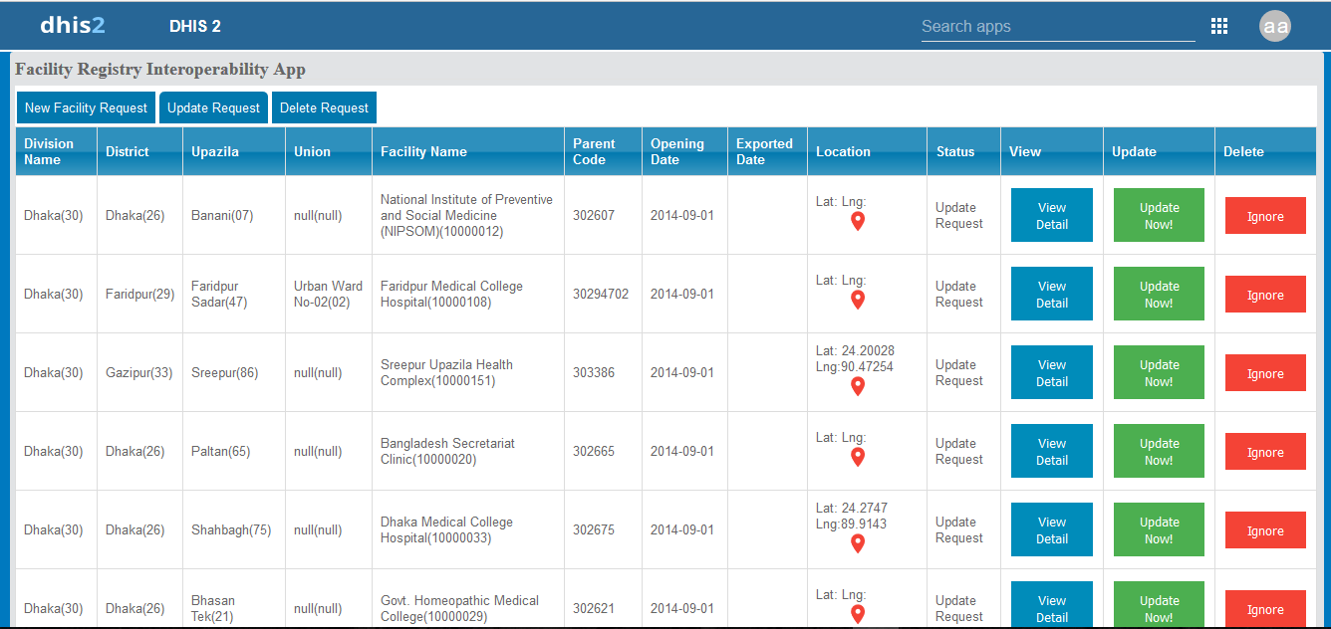
This project focused on developing a robust DHIS2 Middleware application designed to enhance interoperability between national Facility Registry systems and DHIS2. The solution enables comprehensive facility management processes—including extracting new facility records, updating existing entries, and synchronizing deleted facilities—ensuring that all DHIS2 instances remain accurate and up to date. It also incorporates automated handling of blank or incomplete facility fields, strengthening data quality across integrated platforms.
Additional key features include a centralized notification center for real-time alerts, a GIS-based facility location mapping module, and full interoperability support across multiple DHIS2 instances. The middleware facilitates seamless data exchange with external systems such as the Human Resource Information System (HRIS), offering both automatic and manual modes for data transmission. A real-time log monitoring dashboard provides administrators with full visibility into data transactions, error tracking, and system performance, contributing to improved reliability, transparency, and operational efficiency.
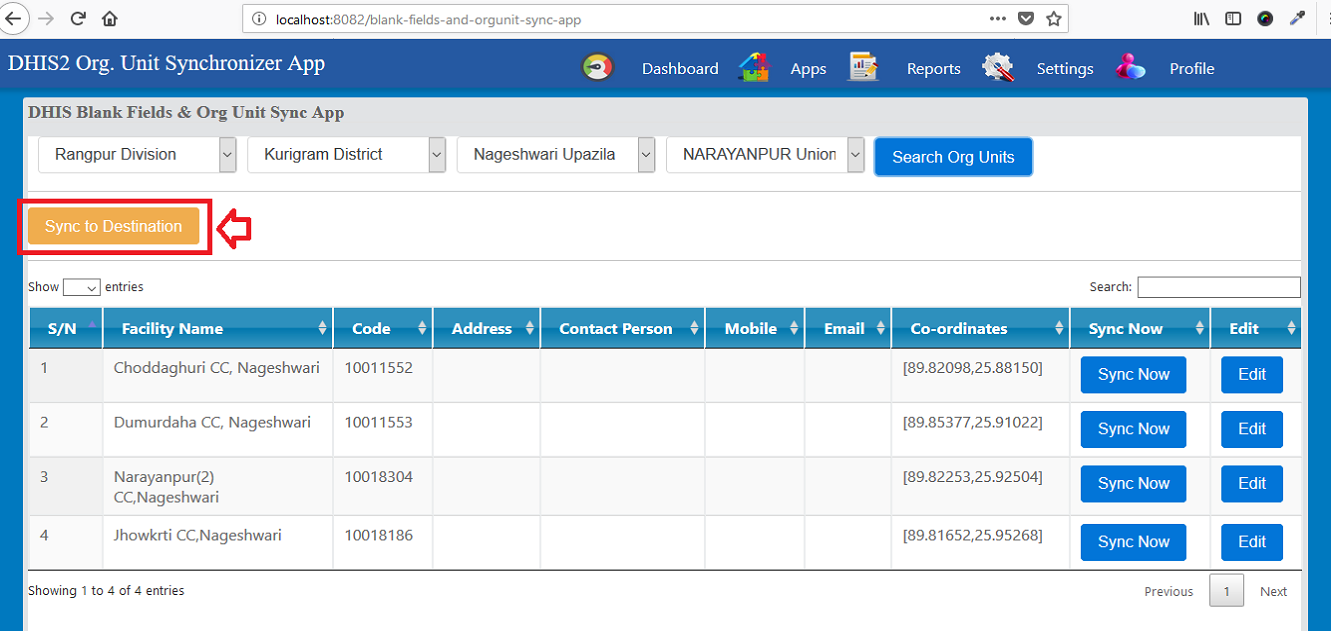
This project focused on enhancing data quality and system coherence within national DHIS2 environments by developing middleware tools dedicated to synchronizing organization units and resolving blank or incomplete data fields. The solution automates the identification, extraction, and correction of missing or inconsistent metadata across DHIS2 instances, helping institutions maintain clean, standardized, and reliable facility information.
In support of robust interoperability, the system enables seamless synchronization of organization unit structures—including creation, updates, and deletions—between Facility Registry platforms and multiple DHIS2 instances. It also provides a comprehensive management interface for handling blank or incomplete facility records, supported by real-time notifications, audit trails, and an integrated GIS component for validating geospatial data accuracy.
The middleware further accommodates both automated and manual synchronization workflows, supports multi-instance communication, and includes real-time log monitoring to track data exchanges and ensure system reliability. This initiative significantly improved metadata integrity, strengthened cross-platform integration, and enhanced national health information system performance.
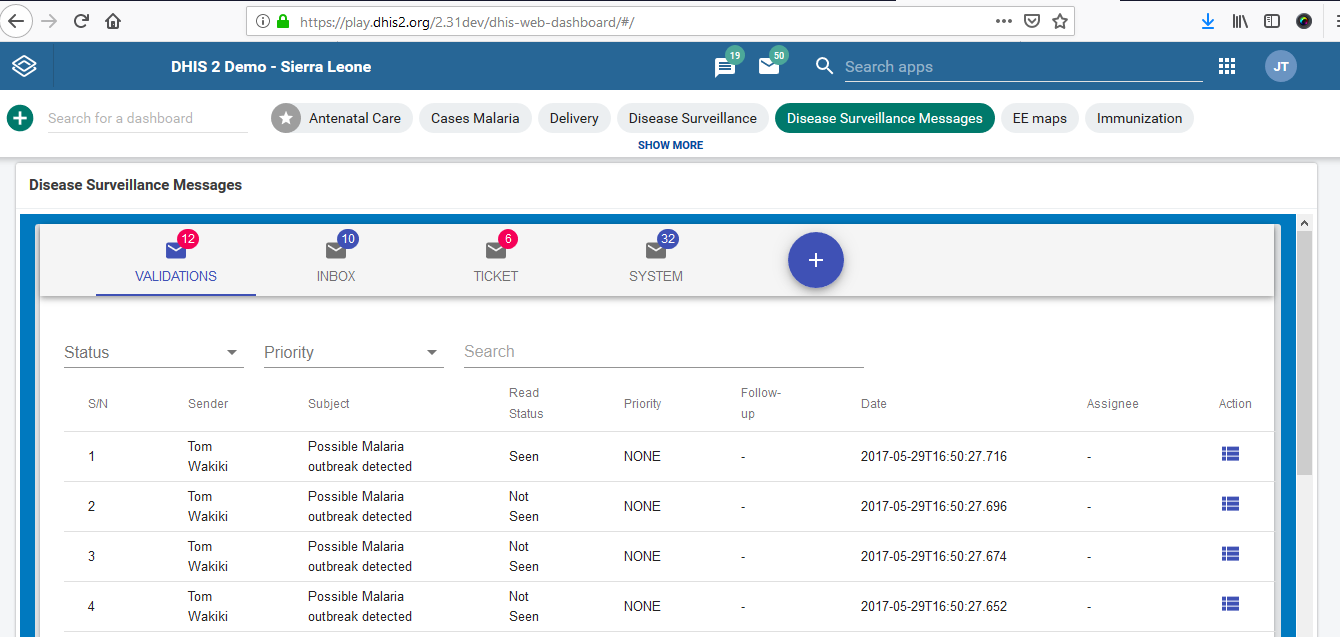
This project focused on the design and development of an interactive dashboard widget to enhance disease surveillance and real-time public health monitoring within the DHIS2 platform. The widget streamlines the visualization of incoming surveillance messages, enabling users to track alerts, notifications, and epidemiological signals with greater efficiency.
Key features include intuitive message categorization, rapid filtering, and dynamic display components that support timely decision-making by national and sub-national health teams. By presenting critical surveillance data directly on the DHIS2 dashboard, the tool strengthens early warning capabilities and improves the overall responsiveness of disease surveillance systems.
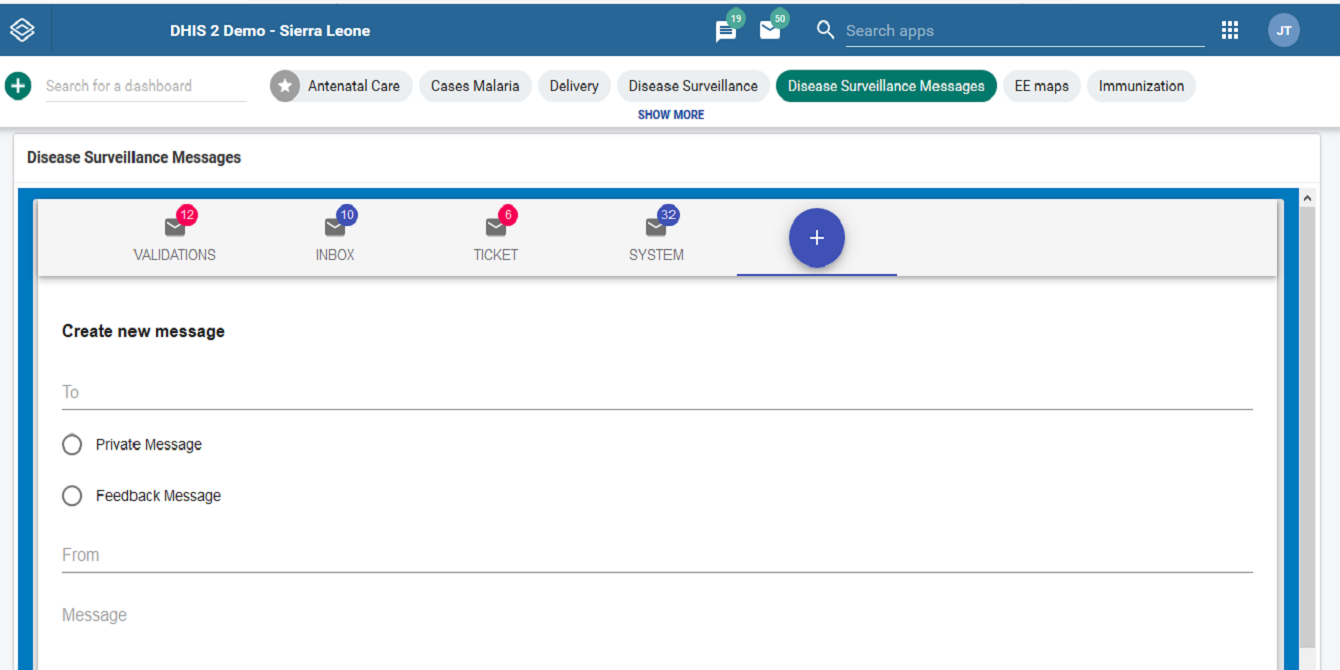
This project focused on the design and development of an interactive dashboard widget to enhance disease surveillance and real-time public health monitoring within the DHIS2 platform. The widget streamlines the visualization of incoming surveillance messages, enabling users to track alerts, notifications, and epidemiological signals with greater efficiency.
Key features include intuitive message categorization, rapid filtering, and dynamic display components that support timely decision-making by national and sub-national health teams. By presenting critical surveillance data directly on the DHIS2 dashboard, the tool strengthens early warning capabilities and improves the overall responsiveness of disease surveillance systems.
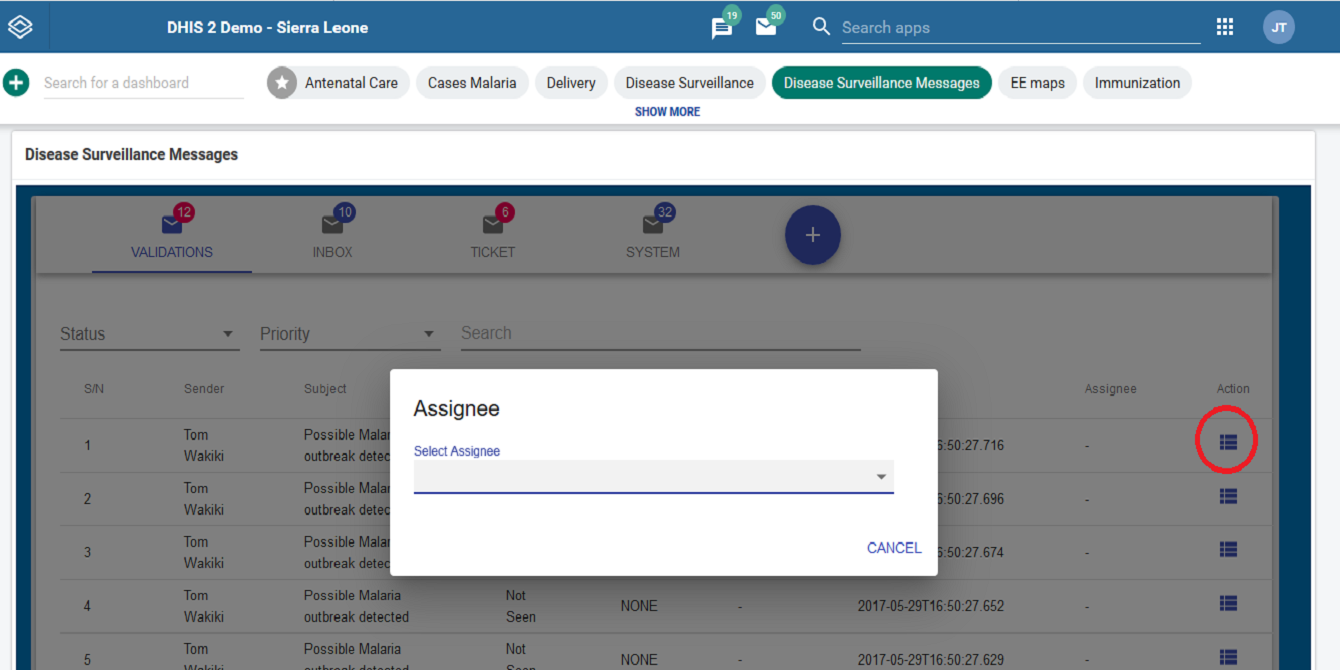
This project focused on the design and development of an interactive dashboard widget to enhance disease surveillance and real-time public health monitoring within the DHIS2 platform. The widget streamlines the visualization of incoming surveillance messages, enabling users to track alerts, notifications, and epidemiological signals with greater efficiency.
Key features include intuitive message categorization, rapid filtering, and dynamic display components that support timely decision-making by national and sub-national health teams. By presenting critical surveillance data directly on the DHIS2 dashboard, the tool strengthens early warning capabilities and improves the overall responsiveness of disease surveillance systems.
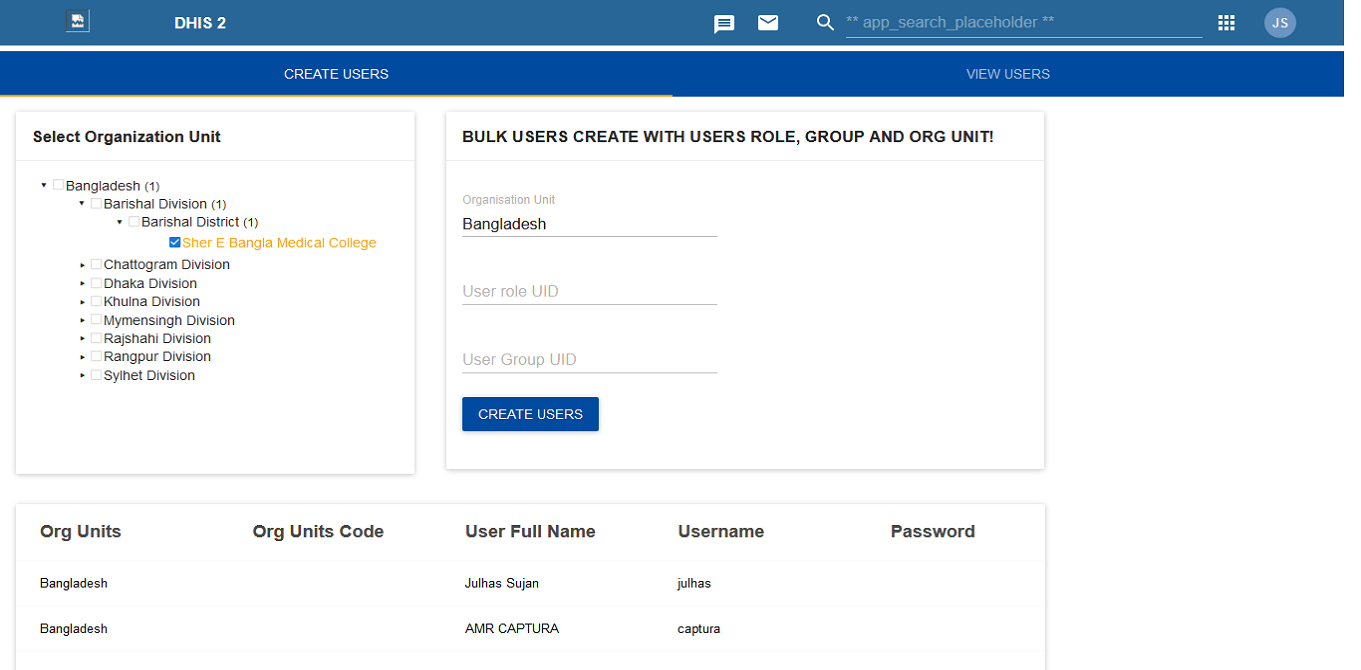
This project involved designing and developing a robust DHIS2 dashboard widget that streamlines the bulk creation and management of user accounts within DHIS2 instances. The widget enables administrators to upload, validate, and import large volumes of user data efficiently, significantly reducing manual workload and minimizing human error.
Key enhancements include automated data validation, intelligent error reporting, support for complex user roles and user groups, and a clean, user-friendly interface integrated directly into the DHIS2 dashboard environment. This solution has improved administrative workflows, strengthened data governance, and enhanced the overall usability of DHIS2 for large-scale implementations.
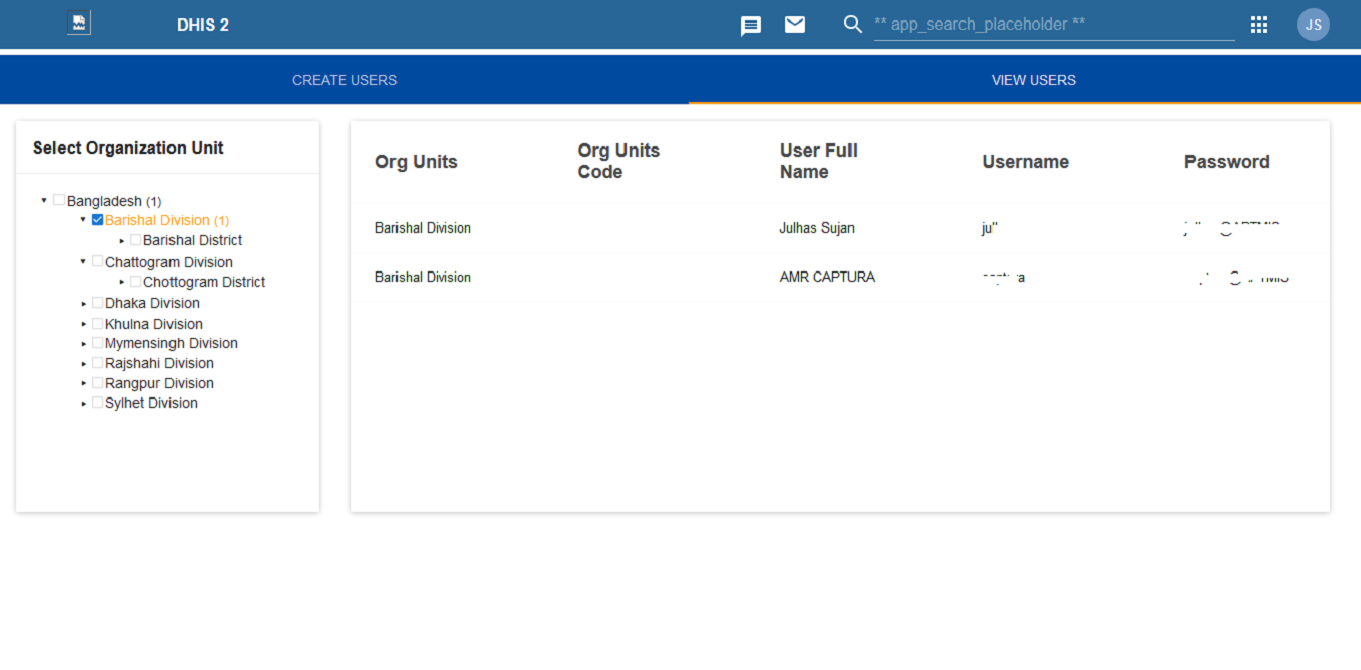
This project involved designing and developing a robust DHIS2 dashboard widget that streamlines the bulk creation and management of user accounts within DHIS2 instances. The widget enables administrators to upload, validate, and import large volumes of user data efficiently, significantly reducing manual workload and minimizing human error.
Key enhancements include automated data validation, intelligent error reporting, support for complex user roles and user groups, and a clean, user-friendly interface integrated directly into the DHIS2 dashboard environment. This solution has improved administrative workflows, strengthened data governance, and enhanced the overall usability of DHIS2 for large-scale implementations.